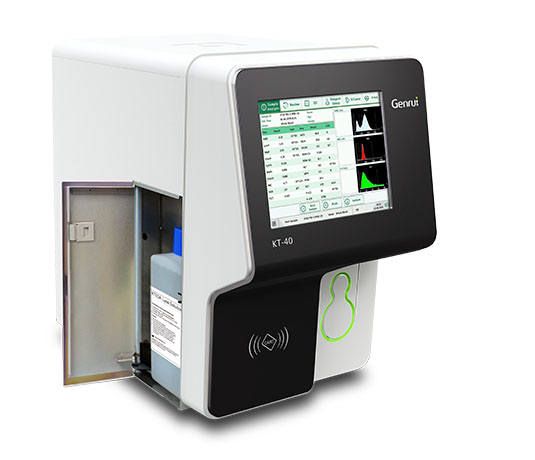
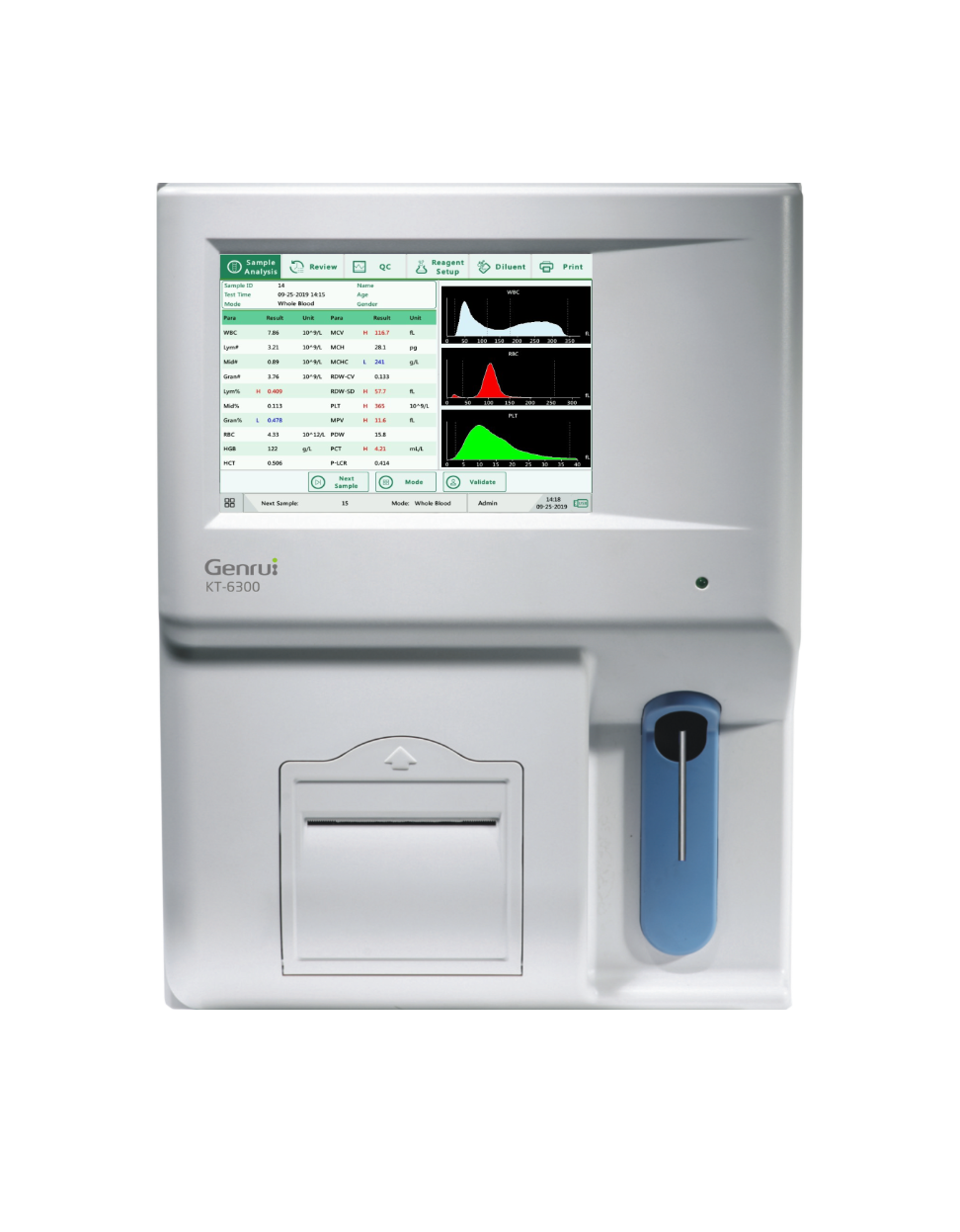
Genrui 3 part differential hematology analyzer uses Coulter's Principle and is able to differentiate between 3 types of WBC's, neutrophils, lymphocytes, and monocytes. In a 3 part hematology analyzer basophils and eosinophils cannot be differentiated and are grouped with a population of either neutrophils or monocytes.
Genrui also has a 5 diff hematology analyzer coping with different testing requirements.
Feb, 10, 2025
Nov, 15, 2024
The traditional method for counting cells is electrical impedance, also known as the Coulter Principle. It is used in almost every hematology analyzer. Whole blood is passed between two electrodes through an aperture so narrow that only one cell can pass through at a time. Then changes in electrical resistance are produced by a blood cell passing through an aperture sensor.
Flow cytometry is a laboratory method used to detect, identify, and count specific cells. This method can also identify particular components within cells. This information is based on physical characteristics and/or markers called antigens on the cell surface or within cells that are unique to that cell type.
The complete blood count (CBC) is a group of tests that evaluate the cells that circulate in the blood, including white blood cells (WBCs), red blood cells (RBCs), and platelets (PLTs). CBC tests can evaluate your overall health and detect a variety of diseases and conditions, such as infections, anemia and leukemia.
A low hemoglobin count is generally defined as less than 13.5 grams of hemoglobin per deciliter (135 grams per liter) of blood for men and less than 12 grams per deciliter (120 grams per liter) for women. In children, the definition varies with age and sex.
 10
10Feb.10, 2025
Live From Dubai: Genrui at Medlab Middle East 2025 15
15Nov.15, 2024
Live From Düsseldorf: Genrui at Medica 2024 02
02Aug.02, 2024
Live From Chicago: Genrui at ADLM 2024